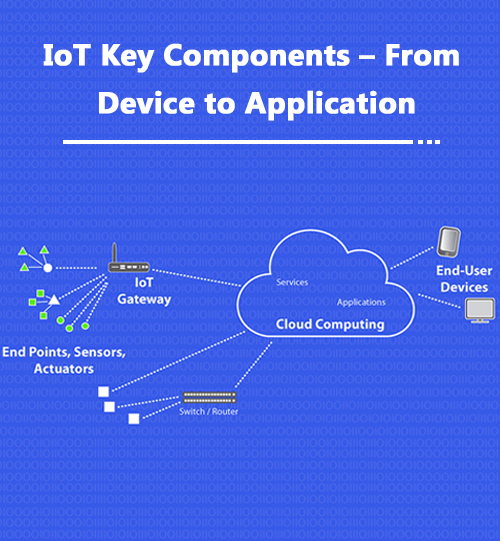
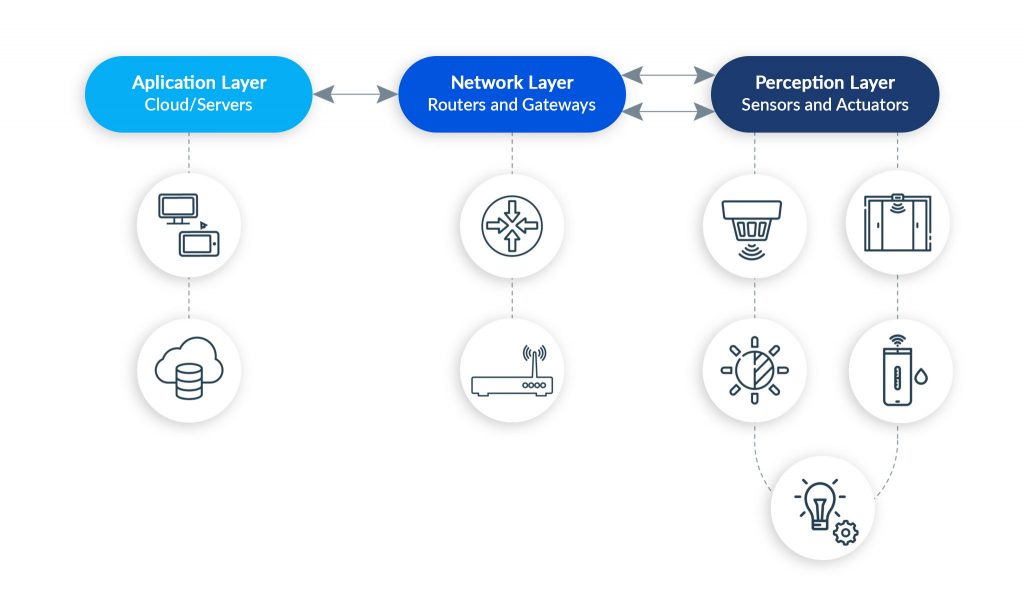
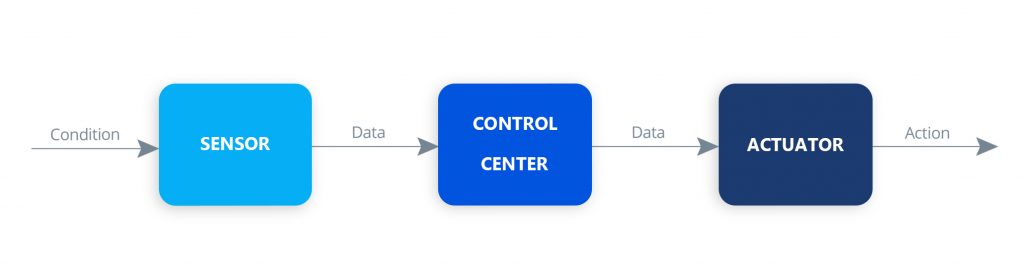
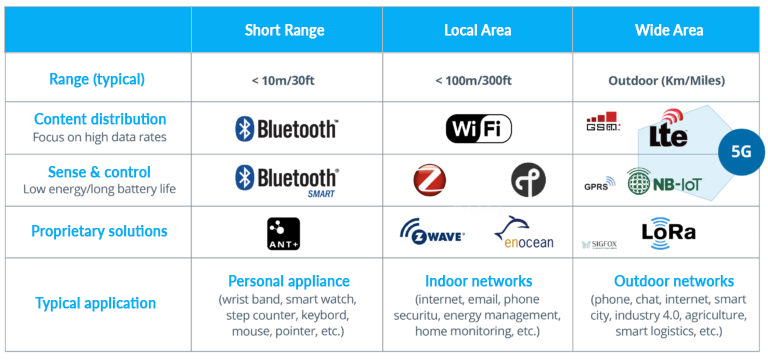
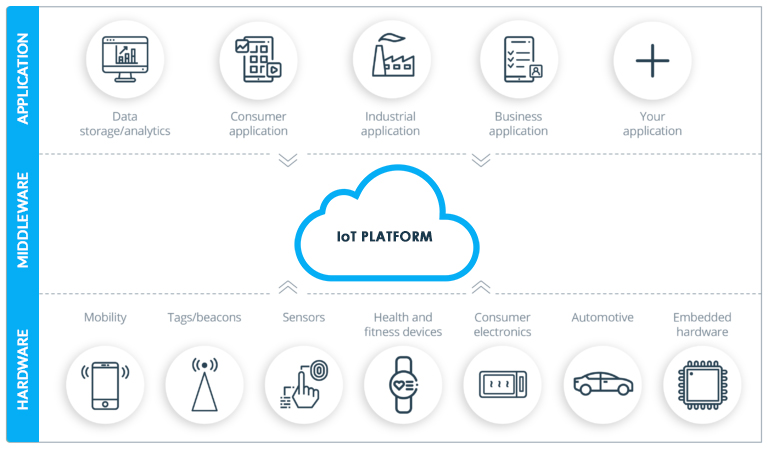
Earlier, establishing connections beyond a single point was a strenuous task. It used to require high-cost hardware solutions and software implementations to connect in-between spaces needed for device-to-device communication. With the advancement of IoT platforms, IoT app developers have started to adopt a low-cost, low-power approach i.e., Wireless mesh networks, to bridge the gap between these devices.
What is a Wireless Mesh Network?
In a mesh network,
infrastructure nodes are connected wirelessly. These nodes further connect to a
host of other nodes to facilitate data communication. Since every device has at
least two ways to transfer data, the whole network doesn’t have to rely on a
single node only.
On the contrary, the
conventional star network is a way in which all the devices are directly
connected to the gateway. Thus, the whole structure becomes very dependent and
prone to connection failures. Besides, the crash in one node connection impedes
the data transfer in the entire network.
Therefore, businesses are more likely to rely on a mesh network instead of a star network.
Working of a Mesh Network
Depending upon the
standard type used in a mesh network, 2-4 different components come in handy.
Nodes –
Every mesh network has nodes i.e., the devices that communicate data with each other.
Gateway –
Gateway not only allows devices to transfer data in the network but also provides a backhaul to the internet for the local mesh network.
Repeater –
In the case of wifi type of mesh network, there are repeaters that maintain internet signal and forward messages between endpoints.
Endpoint –
Endpoints are mesh-only devices that don’t route messages for other devices, but send them to other nodes. That’s why they are referred to as endpoints. Specifically, they have no networking responsibilities, can enter sleep mode, and are excellent components for battery-powered nodes and sensors.
Mesh network for IoT
devices transfers data in two ways: Flooding or Routing. In Flooding, all the
nodes act as a data broadcaster. Thus, this technique expedites data
communication. However, Flooding is an energy-consuming approach.
At the same time, routing chooses one path and transfers the data package from node to node until it reaches the endpoint. Unlike flooding, routing sends data to one node at a time. It chooses another route only when the connection in the first route breaks. Furthermore, to ensure efficiency, the mesh network adopts Shortest Path Bridging i.e., SPB or IEEE 802.1aq algorithm, to transfer data via the shortest route available.
Types of Mesh Network
In a mesh network for IoT devices, IoT app developers can connect devices in two ways: Full Mesh Network or Partial Mesh Network.
Full mesh network
requires end-to-end connection among every device, router, or switch to provide
a high degree of redundancy and efficiency. Besides, it facilitates data
package communication by single-link.
On the other hand, in a partial mesh network, devices are not directly connected to each other. But still, each device is connected to at least two other nodes. So, this type of mesh network enables rapid data transfer from one node to the other.
Benefits of Mesh Network in IoT
Mesh Network for IoT devices offers enormous benefits that make it sought-after in enterprises and significant in an IoT app development company.
Self-healing
Like Shortest Path Bridging, Self-healing algorithm automatically chooses the best path to transfer data even if a few nodes lose connection. Specifically, it uses only those connections that are available and working to maintain the task.
Self-configuring
Due to auto-discovery, mesh networks are self-configuring in nature. Hence, the new nodes calibrate automatically and connect to the network without any previous setup. Consequently, network administration and expansion become easier in mesh networking.
Scalability
and Reliability
In a mesh network,
it is way easy to add or remove nodes without any efficiency issue. Usually,
issues are in proportion to the devices. However, it is quite the opposite in
the case of a mesh network. Adding nodes in a mesh network provides more routes
in which data package can travel, which makes the network faster, reliable, and
error-resistant.
Cost
Reduction
Since mesh networks
don’t require internet connection, it consumes ultra-little energy. Meanwhile,
sensors are pocket-friendly and long-lasting.
Besides, IoT
implementation reduces expenses in many other ways like better management,
optimization of resources usage, and more.
Drawbacks of Mesh Network in IoT
Though there are
ample benefits of a mesh network, it also comes with a few drawbacks. So, it is
essential to gain in-depth knowledge of this network before deciding whether a
mesh network is a perfect fit for you.
Low
Capacity
Mesh network is the
best way of sending small data packages. Unfortunately, it doesn’t perform well
while transferring video file sized data.
Still, if
transferring a large amount of data is compulsory, then the wifi mesh network
would be a better option.
Latency
Actively switching
from one node to another can decelerate the data receiving process. However, it
is not an issue when your system requires a package every few minutes or so.
But, it might be not enough for a few systems.
Conversely, a full
mesh network can accelerate the data transfer by connecting every node to one
another.
Maintenance
Due to the
self-healing ability of the mesh network, finding a non-working node might be
time-consuming. Also, we won’t come to know if a node is having an issue.
On the other hand, mesh
networks for IoT devices are established to make the IoT system smarter and
more efficient. So, the nodes are less prone to crash.
Where IoT Mesh Network Can be Used
With new technologies, wireless mesh networking has reached a point of maturity and become ideal for IoT app developers. Besides, the elevation of connected homes and industry support on open-source resources has made mesh truly accessible and low-cost. They are also regarded as much more viable and real choice for commercial as well as industrial IoT apps. At the same time, it can render extra services in a system where extending a two-node connection is limited.
Smart Cities –
A wireless mesh network is the best for extending radio signals through campus grounds, business parks, parking garages, and other outdoor facilities. Besides extending signals throughout the whole space, it can be able to send a message when a spot is occupied. Thus, areas like parking garages that need space availability checkers significantly benefit from a mesh network.
Healthcare Equipment –
A mesh network can facilitate monitoring and locating medical equipment. It can also serve as a backup for medical devices that always require to stay online. Thus, if one node crashes and loses connectivity, another node can step in to maintain the connection.
Smart Home –
You can track and manage temperature across your home using a wireless mesh network. You can also capture live data and adjust settings automatically by setting up one powered gateway, sensors, and mesh-enabled nodes in each room.
Farming –
Mesh networking is the best way to track sun exposure and water levels across the crops and fields. Additionally, you can create a cellular-connected IoT platform by building a mesh network across a whole acreage with the help of an IoT app development company.
Is Wireless Mesh Networking Right for You?
Before choosing a
mesh network for your IoT project, you must take three core variables into
account: installation, device management, and support.
Installation –
Installation of mesh network depends on your intended app. You need to figure out if you need a distributed set of mesh nodes for your project. Furthermore, if you plan to deploy mesh for industrial or commercial apps, set up a small-scale mesh network to discover the system efficiency before implementing a large-scale mesh network system.
Device Management –
A mesh-enabled IoT solution allows you to manage fleets of devices, perform diagnostics, monitor event logs, and send updates wirelessly.
Support –
Before investing in a mesh solution, it is a wise idea to take the community surrounding it into consideration. Mesh networks with limited adoption have fewer resources available to help you in development.
The Bottom Line
Mesh Network is an essential component for IoT infrastructure as it allows devices to cover more area as well as garner more data. If you are planning to incorporate wireless mesh network into your IoT architecture, examine the entire IoT system, instead of a single component.
Besides, to build an end-to-end IoT product, you need to integrate hardware, software, connectivity, and research IoT platforms that can provide these components.
With this in mind, we suggest consulting experienced IoT app developers who can help you to scope these three complexities and develop a high-quality IoT product.